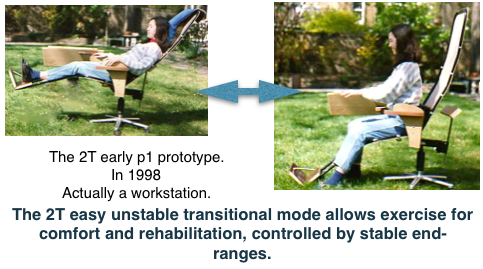
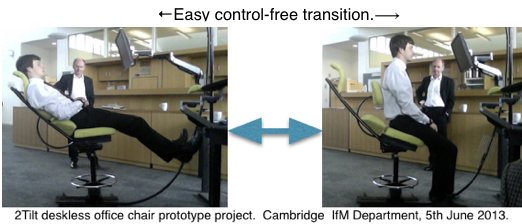
A 2Tilt concept Upright Mode is subsidiary but essential to allow the reclined mode to be fully and easily used in an office or work environment. An unstable Transition Mode has health benefits and it’s importance is described.
Upright mode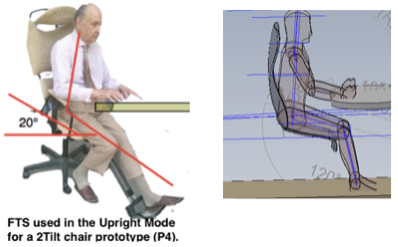
The 2T upright mode is subsidiary but required for certain short activities and quitting the chair and is the default mode when the chair is unoccupied.
The upright mode is for short tasks only and the configuration is unimportant providing that the intermediate, transitional range is unstable.
- Maintaining the wedge angle of the lower two lumbar joints, in the upright mode, can be achieved by a ☛forward tilted seat (FTS)
- or by correct use of ☛ iliac support. The latter cause additional design problems in this case and so is not recommended for an original design but may be convenient for modification of an existing model.
- also see ☛the Ischial off load system→.
An unstable transitional mode.
2T Principle 3.Requirement 8. Mid ranges should be unstable and easily negotiated. It is necessary to be able 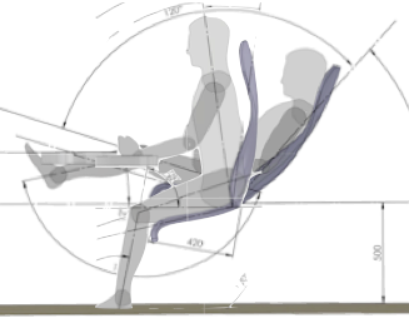 to switch rapidly and easily from a reclined to the upright mode2T mid range.
to switch rapidly and easily from a reclined to the upright mode2T mid range.
- This is mainly for convenience but the switch also results in a change of pressure on the disc and this has the added advantage of providing a pumping action which aids disc nutrition.
- Their instability can be used for short periods as a form of exercise ( ☛dynamic seating→)
- This is not just a quick transition from the reclined to the upright modes (2T) but the instability provides physiological benefits and is itself a mode. The concept is renamed the Tr-Modal (3M). 2T = 3M.
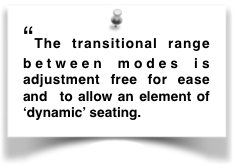
2Tilt Principle 3 Requirement 9. No adjustment is allowed to maintain an intermediate position. The adverse intermediate upright position should be unstable. This allows an easy and rapid transition from one mode to the other and no adjustment is allowed to maintain an intermediate position.
This may seem counter-intuitive. Why shouldn’t the user be able to sit easily in any position that seems comfortable? It worries chair designers dreadfully although they may not be bothered by the ‘dynamic seating’ concept..
Why?
- It is, equivalent to the mid upright position of most office chairs, carrying an ergonomic penalty. A user, used to a mid-upright chair, could use an adjustment to maintain this position for long periods which would add an unnecessary adverse effect to an otherwise optimal system.
- The intermediate positions being unstable require muscular effort to be sustained. On moving back a few degrees from the stable forward upright mode the occupant enters this upright unstable position which provides proprioceptive feedback and frequent small amplitude pressure changes.

- Spinal movement & change of position are important for a number of reasons including IV disc nutrition. ☛ Movement & exercise→
- Particularly for rehabilitation of the Multifidus (☛ muscles→) following an internal derangement at the low lumbar joints.
- A user has a choice and may find a short episode of this low amplitude exercise pleasant. Longer periods are liable to be tiring.
- There is also an added advantage in providing therapeutic exercise following an acute LBP episode with it’s resultant muscle and reflex atrophy. (See ☛Anatomy/muscles).
- Addition of a sit/stand mode in the 3M version allows the user to walk around.
- ‘Dynamic Seating’.Recently there has been interest in continuous small amplitude movement for upright chairs, the chair re-aligning with the users centre of gravity. ☛ Movement & exercise→
- 2T exercise and movement systems ☛ Movement & exercise→
- Sit/Stand. Bio-mechanically superior to the use of existing upright chairs and can be an adjunct to the 2T system which then becomes a ☛ 4M work-station→ concept (and a ‘full’ solution).☛ Sit/Stand→
A specific illustration
 The ALTMARK Chair has both a reclined and upright mode which makes it interesting and ahead of the market. The webpage shows a fixed intermediate position in both the reclined and semi upright modes. At best it gives no biomechanic advantage and was probably intended to add comfort → . Misled by ” that treacherous guide which only turns up truthfully when the ergonomics are fully correct”. If this mode becomes a part of the unstable intermediate mode it allows a faster transition and also gives the user the choice for dynamic motion and rehabilitation. A win-win. Scrapping a fixed intermediate mode reduces manufacturing costs. A win-win-win! Further described in WORK-CHAIRS, a new breed with a reclined mode→.
The ALTMARK Chair has both a reclined and upright mode which makes it interesting and ahead of the market. The webpage shows a fixed intermediate position in both the reclined and semi upright modes. At best it gives no biomechanic advantage and was probably intended to add comfort → . Misled by ” that treacherous guide which only turns up truthfully when the ergonomics are fully correct”. If this mode becomes a part of the unstable intermediate mode it allows a faster transition and also gives the user the choice for dynamic motion and rehabilitation. A win-win. Scrapping a fixed intermediate mode reduces manufacturing costs. A win-win-win! Further described in WORK-CHAIRS, a new breed with a reclined mode→.
Next, return to The 2Tilt RECLINED MODE for fully safe sitting. → or check the effects of The upright seated posture. →