- I was warned in Cambridge to avoid discussion of medical applications of the 2T concept as this might detract from it’s major office use. However it could change the hospital experience for the better. It might also improve the NHS finances!
There seem to be 5 areas with overlapping needs for which a 2T Concept has a perfect application :-
- Mass emergency. With the distressingly increasing frquency of international outrages which involve high volume of casualties which are tended while lying on the floor, a light emergency bed is required.
- A Hospital resuscitation unit.
- Hospital A&E trolley
- Hospital bed
- For specific hospital requirments such as neck traction.
OPTIONS & DETAIL NOTES
- A lightweight bed for emergency use.
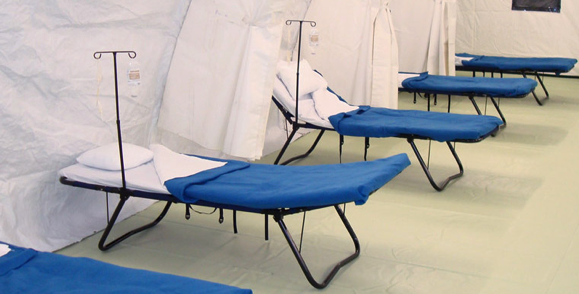 It certainly has advantages over the beds illustrated, BLU-MED’s Portable Ward Beds for Mobile Hospitals has 1-inch aluminium tubing, Weighs only 17-pounds, including IV pole, mattress and decking and Folds to 32-inches x 42.5-inches x 4-inches. This is impressive but, in addition, a 2T version would be more versatile with a wheelchair mode giving easy mobility. The 2T prototypes also used 1″ tubing, slightly heavier, using steel, but probably stronger and more stable.
It certainly has advantages over the beds illustrated, BLU-MED’s Portable Ward Beds for Mobile Hospitals has 1-inch aluminium tubing, Weighs only 17-pounds, including IV pole, mattress and decking and Folds to 32-inches x 42.5-inches x 4-inches. This is impressive but, in addition, a 2T version would be more versatile with a wheelchair mode giving easy mobility. The 2T prototypes also used 1″ tubing, slightly heavier, using steel, but probably stronger and more stable.
2. A 2T version of a trolley for A&E patients (gurney). A design similar to the p/1 prototype monocoque version is suggested. It is mentioned in the press (30/10/2019) that there might be a big demand for the new patients admitted to the NHS who might be left lying around for long periods on uncomfortable trolleys. A multiple use version is described below.
3. A 2T version of a bed. See Hospital beds→ for a plethora of models. A 2T version would be a major advance on most of them in cost, versatility and comfort.
4. Hospital resus. A similar model to the above but of more robust design. The ability to attend to the patient at a desired height and tilt is an advantage. Rapid position change, particularly the Trendelenberg position, needed quickly in acute episodes, is a major advantage.
Hospital resus. A similar model to the above but of more robust design. The ability to attend to the patient at a desired height and tilt is an advantage. Rapid position change, particularly the Trendelenberg position, needed quickly in acute episodes, is a major advantage.
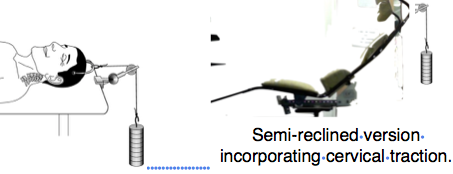
5. Cervical traction. At present the patient lies supine and flat with traction from the skull to a weight attached over the end of the bed. This is prolonged and the position becomes uncomfortable, the constraint is a disadvantage and reading is difficult. With a 2T design the patient can be tilted to a more comfortable, less constrained, semi-reclined position without altering the traction.
6. Patient fitting. A version of the shell for specific needs for individual patients has already been described. A patient would have a shell moulded for the torso that would then be mounted on a suitable version of a 2T chair instead of the standard shell. This addresses the axial compression and pelvic tilt in the reclined mode. In the upright mode the backrest stand away from the torso with a Forward Tilted seat and so becomes irrelevant. But support might be needed and then we would have to think about Gorman’s Iliac version. This is already built into the standard backrest shell, in a reduced form. Plaster-of-Paris’ (POP) casts are commonly made in orthopaedic and physio departments and can be used to form a shell for the individual from fibreglass or other material at no great expense. 3D printing could be relevant. ☛ ‘Special needs’→
A multi-purpose version of a 2T trolley for A&E patients which provides a low cost product to help the NHS finances and, being ergonomically optimised, provides the greatest comfort , which can also be used
 in a mass emergency,
in a mass emergency,- for emergency resuscitation
- a wheelchair
- Temporary bed.
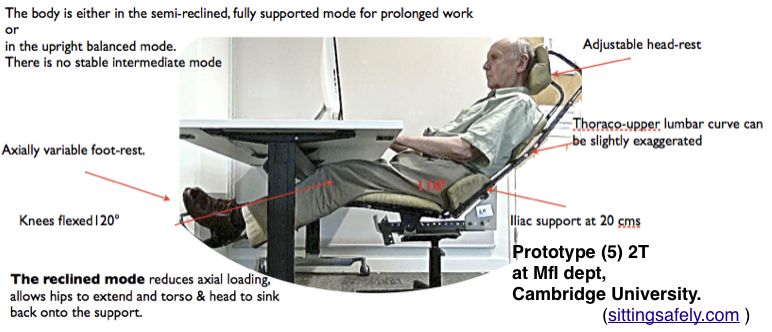
The Cambridge monocoque 2T Prototype 4,  above, was optimised for prolonged office sitting. It also shows a good configuration for an ambulant or semi-ambulant patient. If visualisation of printed matter is not needed then ideally the reclination can be greater.
above, was optimised for prolonged office sitting. It also shows a good configuration for an ambulant or semi-ambulant patient. If visualisation of printed matter is not needed then ideally the reclination can be greater.
It can be used to illustrate of the variatons need for a trolley/emergency bed.
- The 2T principle 8, for an office chair, has to be modified to allow Fixed adjustment stable positions in the transitional mode at the hinges.
- Requires hinges at
- Back-rest/seat pan.
- Seat pan/Leg-rest
- This is needed to provide
- An upright (wheel chair) mode,
- A straight horizontal mode for a user to lie prone or on side.
- Also Retain the position ergonomically optimised (as above).
- Length adjustment is required for headrest and leg rest (as in the 2T concept)
- Rotation of, say, 20°, to allow a user to quit the trolley without having to move it away from the wall.
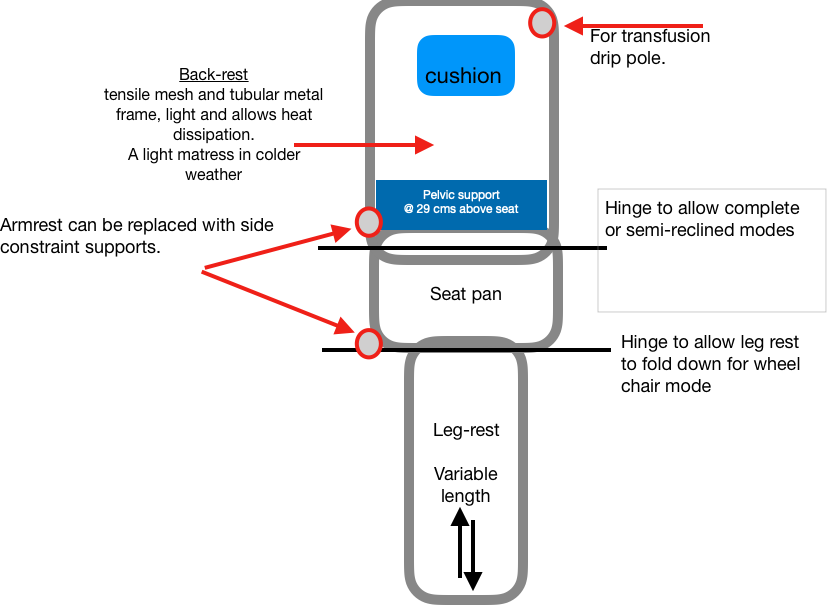
- Advantages A 2T version has advantages
- Simple and inexpensive
- For storage and logistics it can be easily disassembled, sterilised and stacked.
- Allows an upright (wheel chair) mode,
- Semi-reclined mode. As for the 2T chair version, for comfort.
- The patient can lie comfortably supported when lying supine and can be in a sitting position..
- Strait, full, supine mode modification without semi-reclination is also needed.
- Lying on side, fully prone or in the recovery position would then be possible.
- The slight ‘iliac’ support would be lying above the pelvic brim and limit slippage if the head end is lowered.
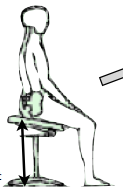
- The slightly elevated legs aids venous return. It can be addressed by increasing the seat/back-restangle or having these components hinged.
- The patient can be effortlessly put in the Trendelenburg position. ( the head is lower than the feet).
- The 2T principle 8 has to be modified to allow stable positions in the transitional mode.
- Manufacture can be inexpensive.
-
- The 2T prototypes all used a standard 5 star base.
- This is not essential but if used needs modification.
- Rotation should be limited, for stability, to 35º in the forward direction.
- The 2 back legs should be extended for stability when reclined.
- They can be used to support a shelf.
- the-2t-base/
From Peter Bessey :-
For a trolley to take most benefit from 2T, I would suggest that it not be fixed, but permit rotation when required. Achieving that and allowing for it safely, within the frame detailing, is the kind of functionality that is likely to take time to perfect. (I need persuading! Extra expense and unneccessary)
Attempting to also value engineer the design, so that it can be manufactured optimally for low budget purposes too, is also the kind of activity that takes time too. But I would anticipate that is needed equally for the NHS, as for disaster-relief instances in low-income countries.
The latter situations could also benefit from a stacking, or folding design, so that minimum volume is taken up during storage, particularly awaiting actual disaster instances, as well as for off-the-shelf use in standard hospital environments too. (The base has to be disconnected from the shell)
Once those types of considerations become desirable and part of the brief’s goals, then the task is somewhat more complex than ‘just a simple gurney’.

 The Ankit model has a simpler base. It is possible to incorporate a hinge mechanism onto this sort of 4 wheel base to support the functional carcass.
The Ankit model has a simpler base. It is possible to incorporate a hinge mechanism onto this sort of 4 wheel base to support the functional carcass. 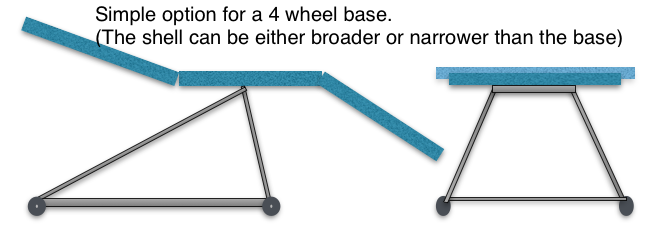

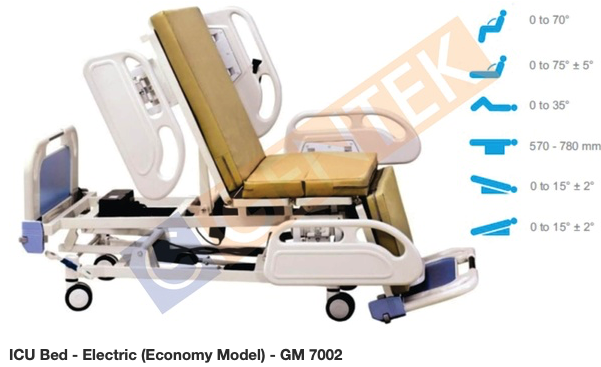

 Ankit
Ankit A simple hospital bed.
A simple hospital bed.
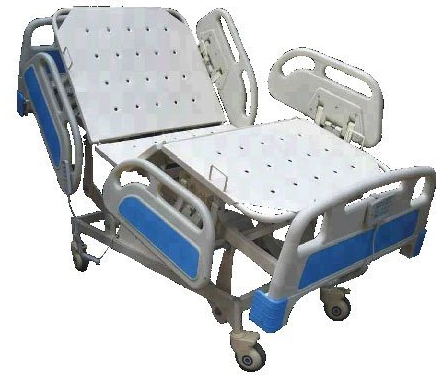
 reading and cleaning.
reading and cleaning. the calf,
the calf, Adjustable head-rest, foot-rest and leg-raise would be integral.
Adjustable head-rest, foot-rest and leg-raise would be integral.

 It can be seen that a 2T version has the potential to be a major advance on most of these in cost, versatility and comfort.
It can be seen that a 2T version has the potential to be a major advance on most of these in cost, versatility and comfort. 
 the home have been rather ignored as their ergonomics are unimportant compared to chairs required for prolonged work. Since looking at chairs from a
the home have been rather ignored as their ergonomics are unimportant compared to chairs required for prolonged work. Since looking at chairs from a 
 The ‘Saddle Chair’ by Timothy Oulton, at his fantastic new premises in the old Bluebird workshop in the Kings Road, caught my eye. It is almost reclined
The ‘Saddle Chair’ by Timothy Oulton, at his fantastic new premises in the old Bluebird workshop in the Kings Road, caught my eye. It is almost reclined  with no other concern for ergonomics. Still on an equestrian theme,
with no other concern for ergonomics. Still on an equestrian theme,  when there is a one- piece solution which could be more elegant, simpler and to the contemporary taste using the 2T (3M) concept. Being more ergonomically compliant it would also be even more comfortable.
when there is a one- piece solution which could be more elegant, simpler and to the contemporary taste using the 2T (3M) concept. Being more ergonomically compliant it would also be even more comfortable.

 The pair from my Uncle Jack (Berrington) during the South African Boer War (c. 1902) was lost in transit so he indented for two more.
The pair from my Uncle Jack (Berrington) during the South African Boer War (c. 1902) was lost in transit so he indented for two more.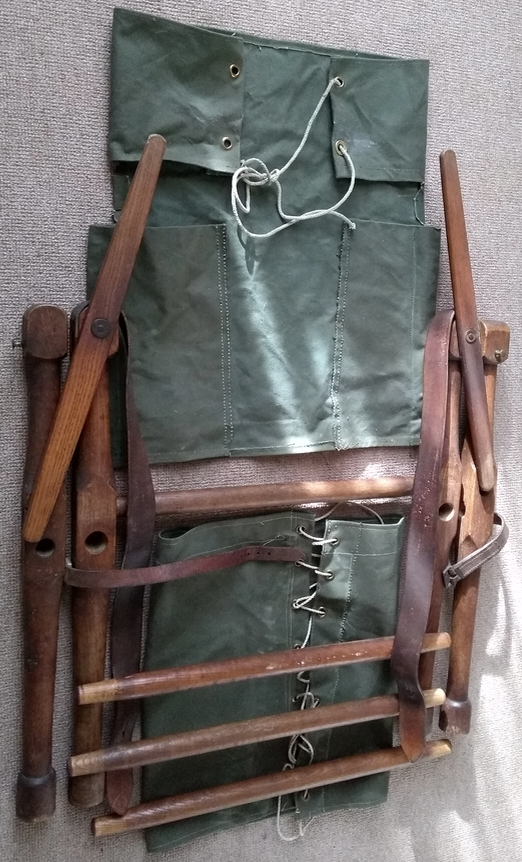
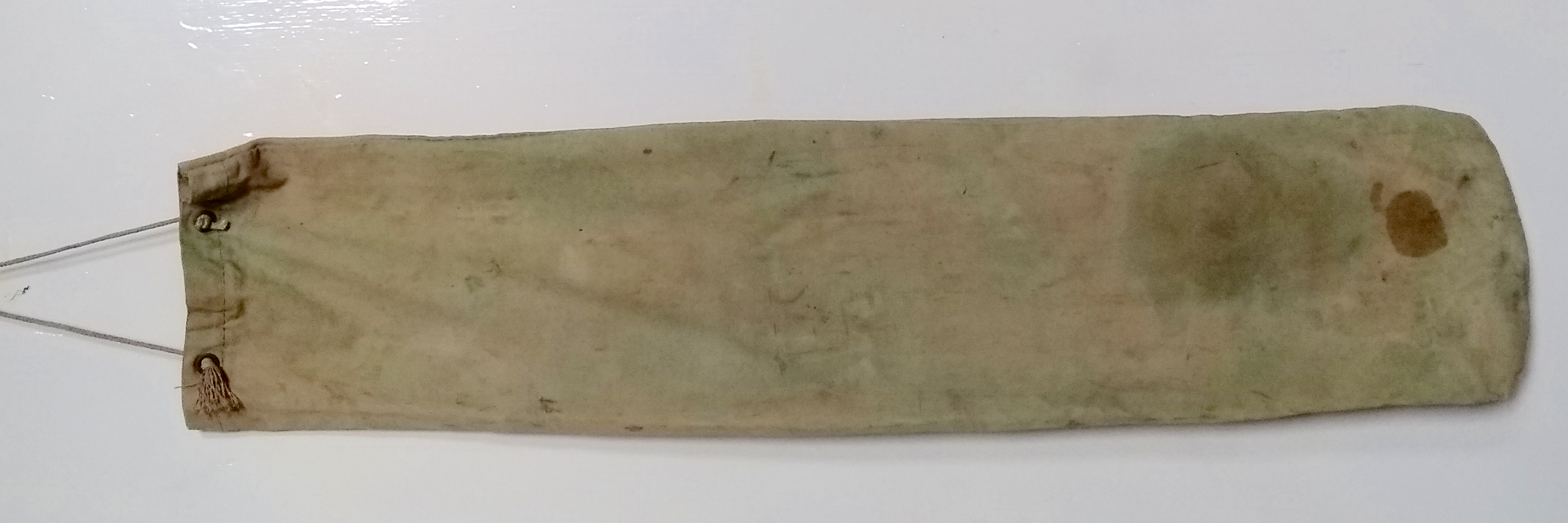 bag. The original bag 90 x 23 cm.
bag. The original bag 90 x 23 cm.
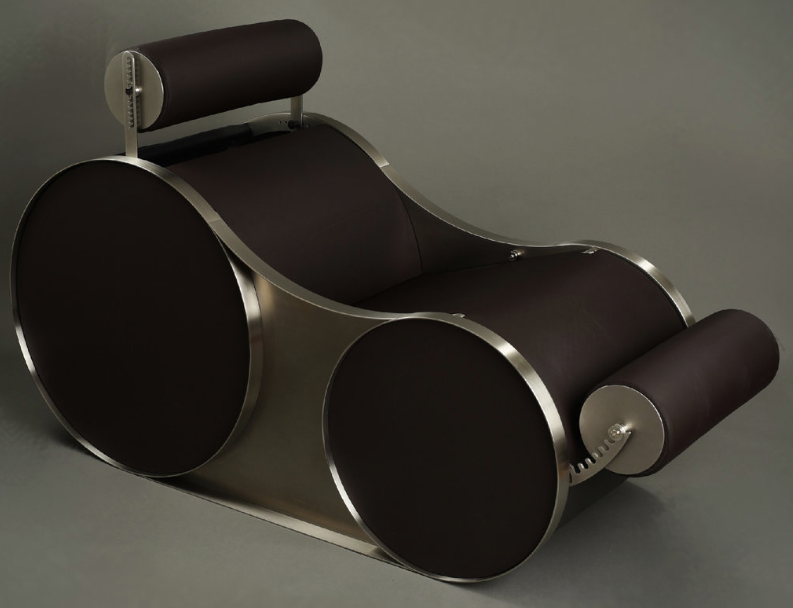





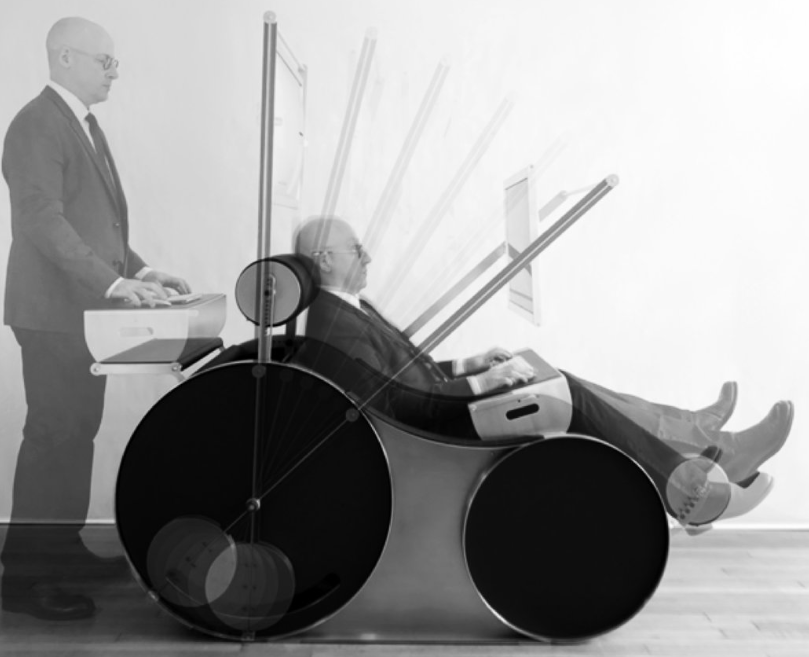 user. If paired with a laptop, the PDI can also be used as a dual-screen interface in both the seated or standing position. With the PDI in the default standup desk position, the Chotto simultaneously accommodates both a standing and seated user – all within a small 15 s.f. footprint.”
user. If paired with a laptop, the PDI can also be used as a dual-screen interface in both the seated or standing position. With the PDI in the default standup desk position, the Chotto simultaneously accommodates both a standing and seated user – all within a small 15 s.f. footprint.”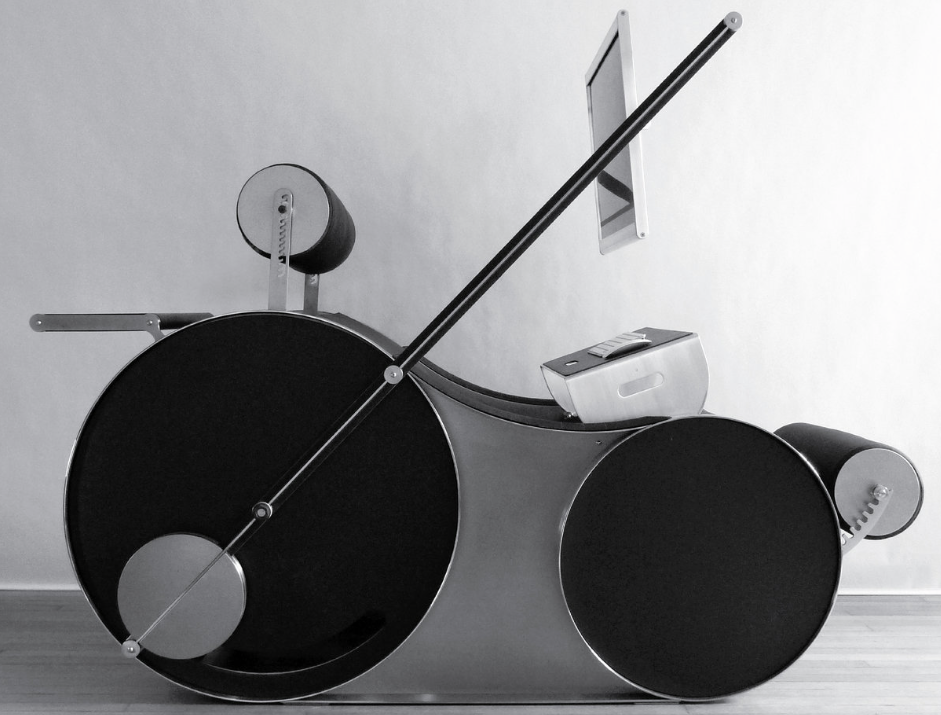
 Architects have a tradition for designing good furniture. Aaron Chetwynd did this 2T sketch for me. It is deliberately ‘office chair’ looking to reduce ‘familiarity bias’. It is not intended to be a work-station.
Architects have a tradition for designing good furniture. Aaron Chetwynd did this 2T sketch for me. It is deliberately ‘office chair’ looking to reduce ‘familiarity bias’. It is not intended to be a work-station.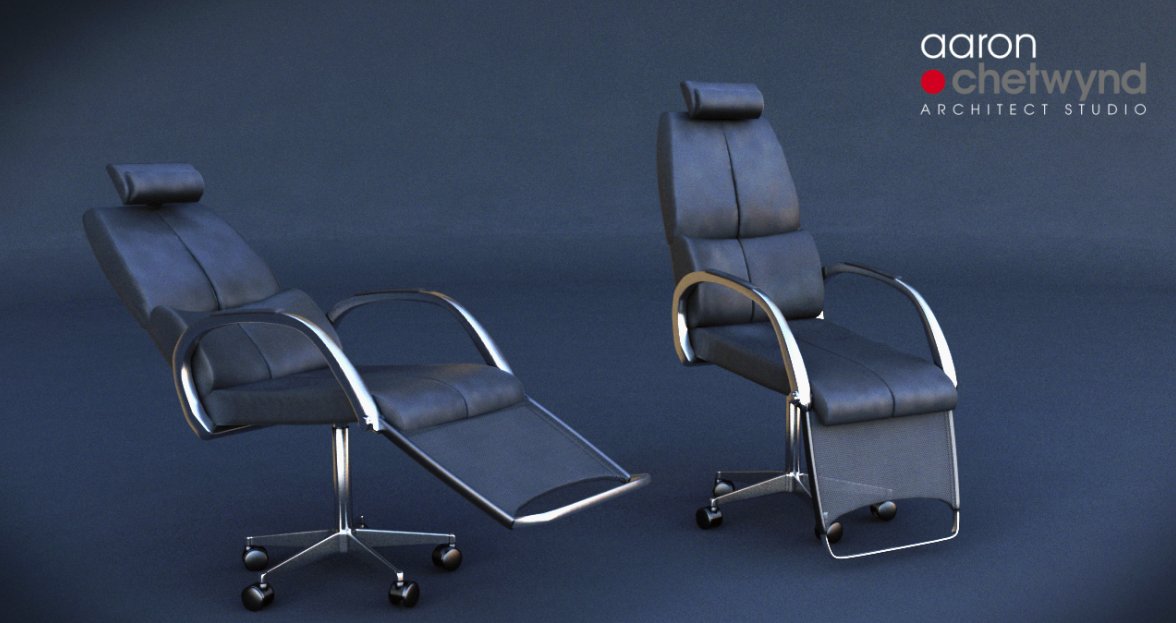

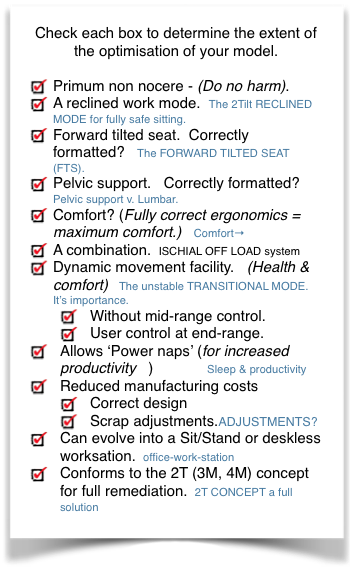
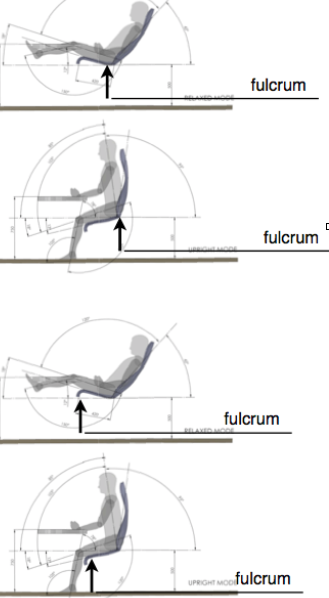
 2T so called as there are only 2 stable positions, each at either end of range.
2T so called as there are only 2 stable positions, each at either end of range.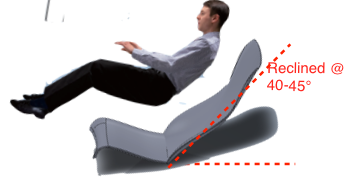
 DETAILS & OPTIONS
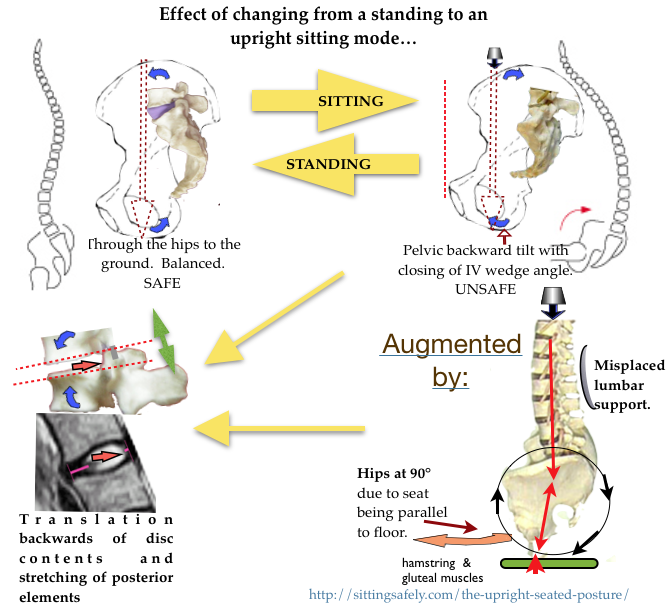
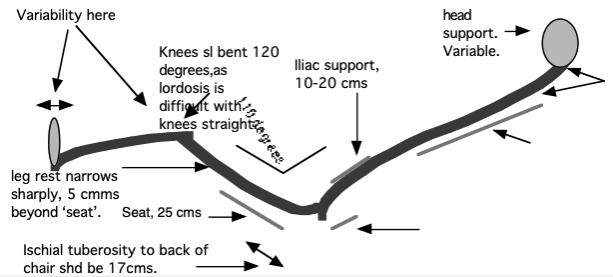
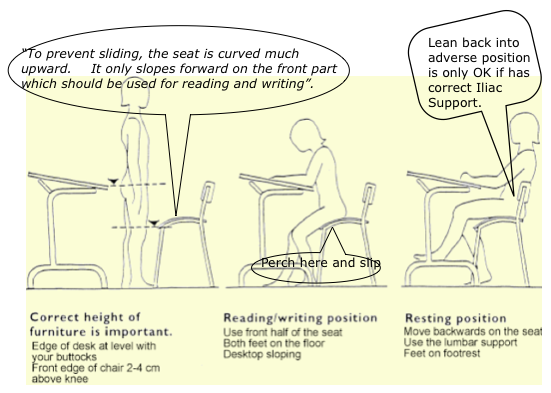
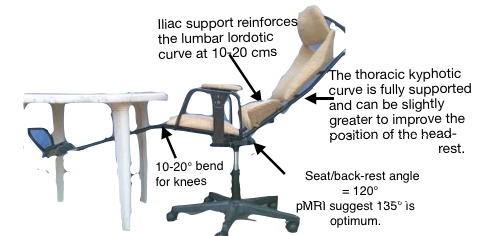
DETAILS & OPTIONS Shows that a slightly flexed thoracic spine + the upper lumbar joints is not adverse.
Shows that a slightly flexed thoracic spine + the upper lumbar joints is not adverse.
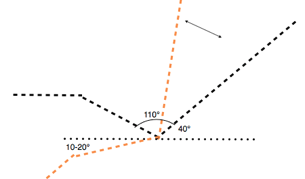

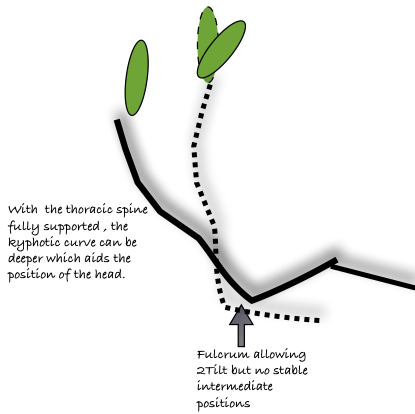 This alternative upright mode is for certain short tasks only.
This alternative upright mode is for certain short tasks only.
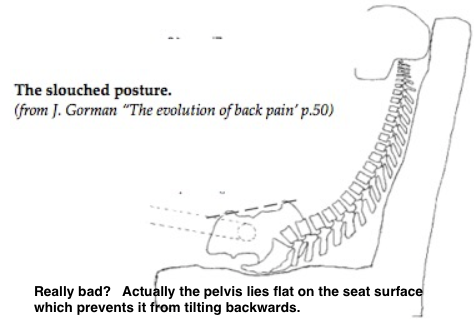
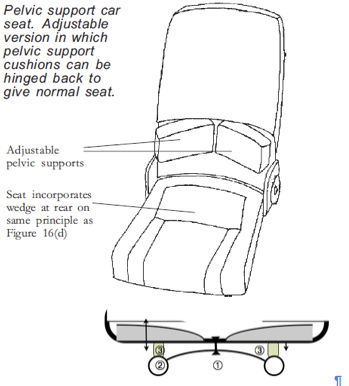 prevent backward pelvic tilting when supine lying. It cease to be ‘pelvic’ and becomes the adverse ‘lumbar’ support above 20 cm from the seat -pan.
prevent backward pelvic tilting when supine lying. It cease to be ‘pelvic’ and becomes the adverse ‘lumbar’ support above 20 cm from the seat -pan. 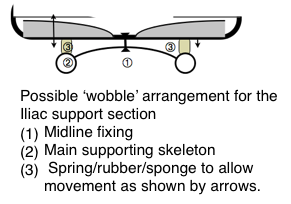
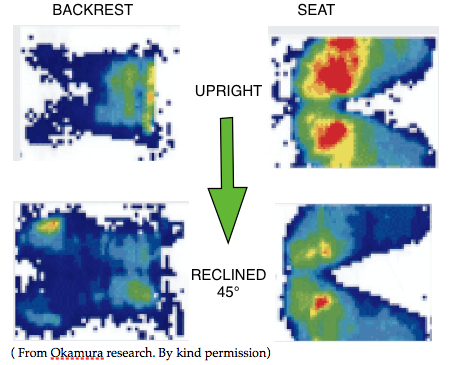 Torso/seat interface pressure studies show that most of the body weight is concentrated at and around the ischial tuberosities. Very little at the thighs, except in the Forward TS mode.
Torso/seat interface pressure studies show that most of the body weight is concentrated at and around the ischial tuberosities. Very little at the thighs, except in the Forward TS mode. 

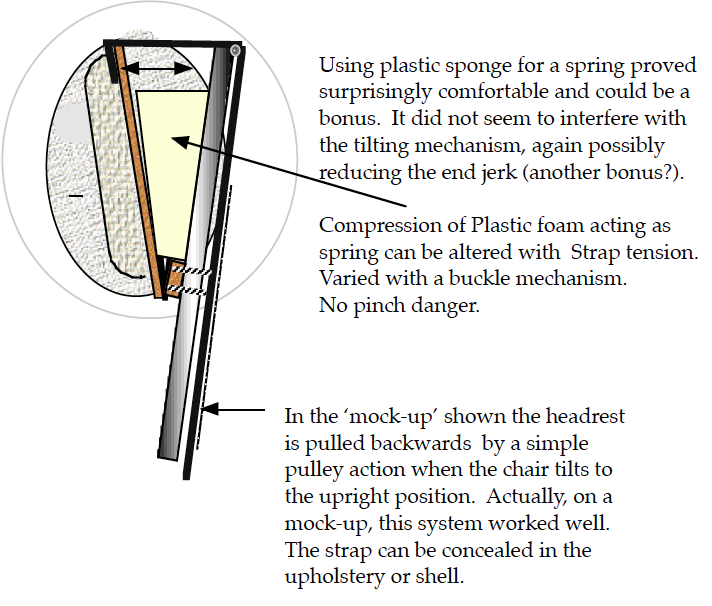

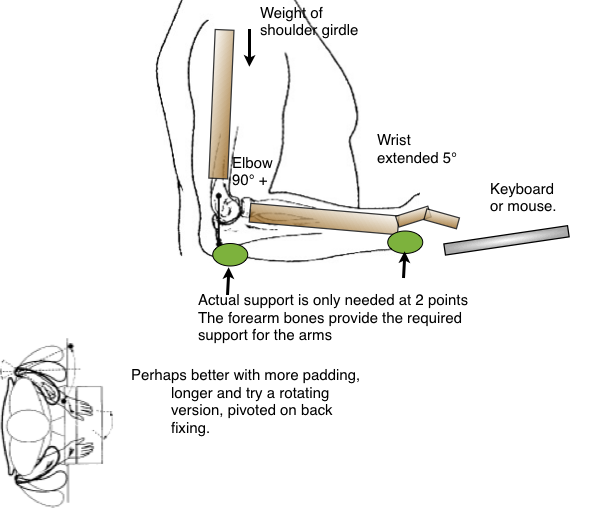
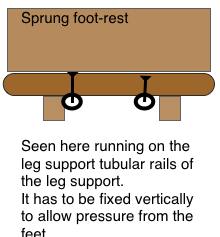 A SPRUNG SOLE MUST BE OPAQUE FOR ISLAMIC SUSCEPTIBILITIES.
A SPRUNG SOLE MUST BE OPAQUE FOR ISLAMIC SUSCEPTIBILITIES.
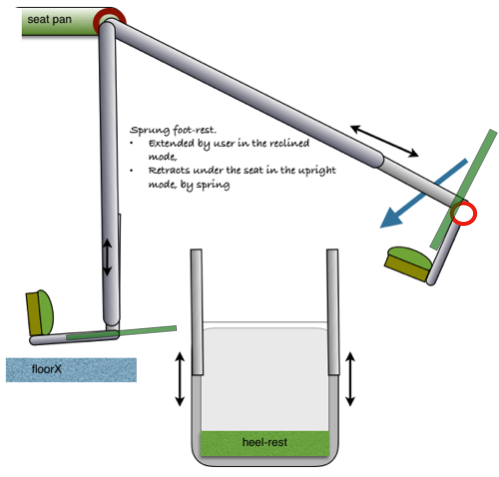
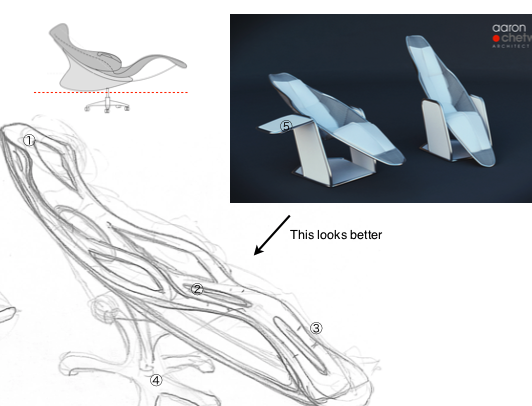
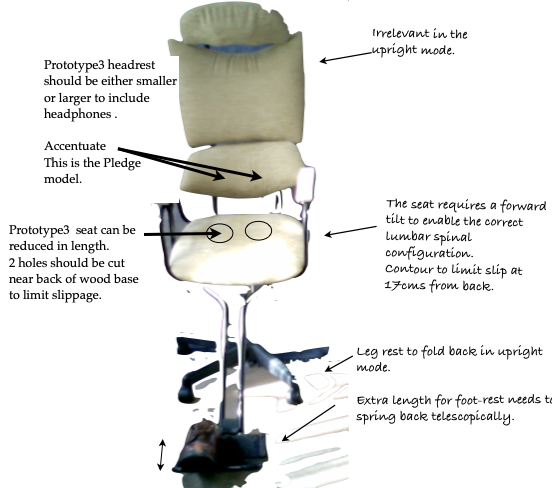
 Details of the p3 prototype.
Details of the p3 prototype.
 It certainly has advantages over the beds illustrated, BLU-MED’s Portable Ward Beds for Mobile Hospitals has 1-inch aluminium tubing, Weighs only 17-pounds, including IV pole, mattress and decking and Folds to 32-inches x 42.5-inches x 4-inches. This is impressive but, in addition, a 2T version would be more versatile with a wheelchair mode giving easy mobility. The 2T prototypes also used 1″ tubing, slightly heavier, using steel, but probably stronger and more stable.
It certainly has advantages over the beds illustrated, BLU-MED’s Portable Ward Beds for Mobile Hospitals has 1-inch aluminium tubing, Weighs only 17-pounds, including IV pole, mattress and decking and Folds to 32-inches x 42.5-inches x 4-inches. This is impressive but, in addition, a 2T version would be more versatile with a wheelchair mode giving easy mobility. The 2T prototypes also used 1″ tubing, slightly heavier, using steel, but probably stronger and more stable. Hospital resus. A similar model to the above but of more robust design. The ability to attend to the patient at a desired height and tilt is an advantage. Rapid position change, particularly the Trendelenberg position, needed quickly in acute episodes, is a major advantage.
Hospital resus. A similar model to the above but of more robust design. The ability to attend to the patient at a desired height and tilt is an advantage. Rapid position change, particularly the Trendelenberg position, needed quickly in acute episodes, is a major advantage.
 in a mass emergency,
in a mass emergency,


 Normalcy bias is slightly different and can lead to serious problems for firms, however big. It is a dangerous trap for manufacturers of ergonomic office chairs, who may be perfectly happy with the status quo, to fall into and it can blind recognition to a very real and credible threat.
Normalcy bias is slightly different and can lead to serious problems for firms, however big. It is a dangerous trap for manufacturers of ergonomic office chairs, who may be perfectly happy with the status quo, to fall into and it can blind recognition to a very real and credible threat.