OVERVIEW. The 2 TILT (or 3M) chair CONCEPT. And 4M.
A complete solution. An optimal system that effectively fully remediates all the adverse effects that have been enumerated. It is the optimised default against which the ergonomics of any chair can be assessed for establishing its ergonomic efficiency. An essential tool for chair design.
Listed here are those effects requiring remediation to ensure a safe sitting position :-
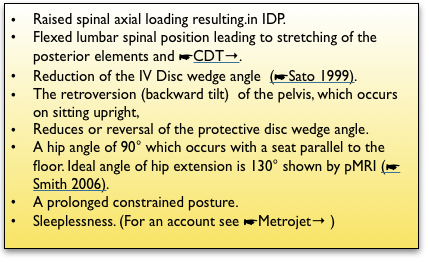
- •The intradiscal pressure (IDP) from spinal axial loading in the upright state. ☛Loading→ Raised IDP has increasing effect with degeneration which occurs in most people and may start surprisingly early. ☛Inter Vertebral Disc (IVD)→
- Additional mechanical factors, such as flexion and rotation are required for disc prolapse to result.
- A kyphotic, flexed lumbar spinal position leading to stretching of the posterior elements and ☛CDT→.
- Reduction of the IV Disc wedge angle (☛Sato 1999).
- The retroversion (backward tilt or to an an anatomist a ‘forward tilt’) of the pelvis, which occurs on sitting upright, reduces or reverses the protective disc wedge angle.
- A hip angle of 90° which occurs with a seat parallel to the floor allowing the hip extensor muscles (hamstring & glutei) to rotate the pelvis so as to flatten the lumbar lordosis. Ideal angle of hip extension is 130° shown by pMRI (☛Smith 2006).
- A prolonged constrained posture.
- Sleeplessness. (For an account see ☛Metrojet→ )
- For a complete account ☛ Remediation→.

-
 A full body support that is configured to the correct spinal shape. (Not detailed here)
A full body support that is configured to the correct spinal shape. (Not detailed here)- The reclined mode requires head support that allows for a forward vision field.
- Variability at head and feet only. Avoided elsewhere. Adjustments→.
- Leg/foot support, which can be provided by the floor if the knees can remain extended. (See the Aeron Atlas chair)
A Reclined mode is the best for prolonged work. The 2T reclined mode→
- An Upright Mode is subsidiary but required for certain short activities and quitting the chair and is the default mode when the chair is unoccupied. ☛2T Upright modes→
-
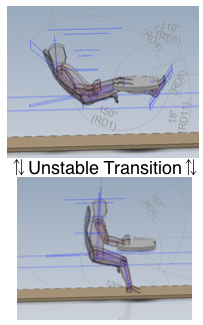 Transitional Mode. The mid ranges should be unstable and easily negotiated ☛UPRIGHT MODE & TRANSITION for the 2Tilt concept →. This is to avoid the conventional adverse mid-upright sitting posture. It can be used for short periods as a form of exercise ( ☛ dynamic seating→), particularly for rehabilitation following an acute attack of Backache.
Transitional Mode. The mid ranges should be unstable and easily negotiated ☛UPRIGHT MODE & TRANSITION for the 2Tilt concept →. This is to avoid the conventional adverse mid-upright sitting posture. It can be used for short periods as a form of exercise ( ☛ dynamic seating→), particularly for rehabilitation following an acute attack of Backache. - This leads on to the QuadriModal, 4M work-station.
- Reduced office footprint.
- 2T requirements easier to achieve.
- Easy to move about & around.
- Allows short periods of sleep ( ☛MetroNaps→)
- 2T in the office and ☛4M work-station→
For further details :-
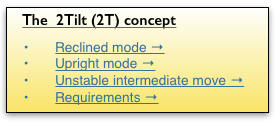

To recapitulate. The identified adverse bio-mechanical factors of Upright Sitting.
Any chair can be compared for establishing the ergonomic efficiency. An essential tool for chair design. It is the optimised default against which the ergonomics of any chair can be assessed.
The fundamental remediation …
Only a reclined posture, basic to the 2Tilt chair concept, can reduce all these and this must be the only logical system for a prolonged working position. The 2T is the default against which the ergonomics of any chair can be assessed. The 2Tilt RECLINED MODE for fully safe sitting.→
 At last, in 2015, a number of work chairs are appearing with a working reclined mode. They seem to ignore the science and lack the efficency, ergonomic optimisation and simplicity of the 2T concept. See New breed of reclined office chairs→
At last, in 2015, a number of work chairs are appearing with a working reclined mode. They seem to ignore the science and lack the efficency, ergonomic optimisation and simplicity of the 2T concept. See New breed of reclined office chairs→
REQUIREMENTS for the 2Tilt concept.
To achieve an efficient working 2T (3M) chair a number of requirements are essential.
Principle 1
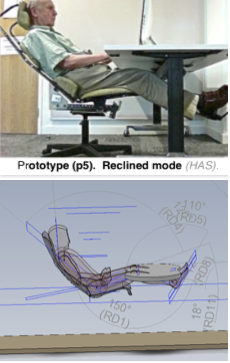 Reclined mode. The optimum for prolonged work
Reclined mode. The optimum for prolonged work
Prolonged sitting tasks should be performed in the reclined position with the backrest at 40-45°
from the horizontal using a normal desk. This can be reduced with a desk-less version. Support is given to the whole length of the body, from head to feet. pMRI studies have confirmed that the risk of posterior disc displacement is avoided by supine or semi-supine positions.(Smith,2006).
In the reclined mode some requirements are necessary to ensure optimal support and must include the following.
- Requirement 1 Support is given to the entire length of the body, from head to feet with a back support correctly configured to spinal morphology, with iliac support at correct level and shape.
- Requirement 2. Even with the reduced axial loading the lumbar lordosis should be maintained and this is best effected by some pelvic (not lumbar) support. This should only be sufficient to avoid lumbar flattening, and should avoid excessive lordosis.
- Requirement 3. Some extra curve (kyphosis) of the thoracic spine, over that which pertains on standing, is allowed because it is fully supported and is a stable area and not liable to mechanical breakdown. It extends, with the upper lumbar joints, over 14 segments and the extra flexion at any single joint is minimal.
- Requirement 4. A correctly placed head/neck-rest is required so that the occupant has no need to move the neck to establish the task-related visual field.
- Requirement 5. It is necessary to have support for the legs and feet. Compression of the calf muscles should be avoided. A spring exercise system is an advantage. The floor is allowed as a foot-rest if the knees can remain extended.
- Requirement 6. Variability at head and feet only. These are the most variable parts of the human body, in the reclined mode. Adjustments avoided elsewhere. ☛Adjustments→.
- A reclined 40-45° position is advised for a stand-alone 2T chair. Greater angle, nearer fully supine, is possible with a deskless work station ☛4M OFFICE WORK-STATION→.
- See ☛The 2T reclined mode→
 Principle 2. (Hence the 2T concept)
Principle 2. (Hence the 2T concept)
A 2Tilt Upright Mode is subsidiary but required for certain short activities and quitting the chair
and is the default mode when the chair is unoccupied. ☛2T Upright modes→ ☞Mandal
• Requirement 7. Maintaining the wedge angle of the lower two lumbar joints, in the upright mode, can be achieved by a ☛forward tilted seat (FTS) or by correct use of ☛ iliac support. The latter cause additional design problems in this case and so is not recommended for an original design but may be convenient for modification of an existing model.
Principle 3. An unstable transitional mode.
• Requirement 8.Mid ranges should be unstable and easily negotiated. It is necessary to be able 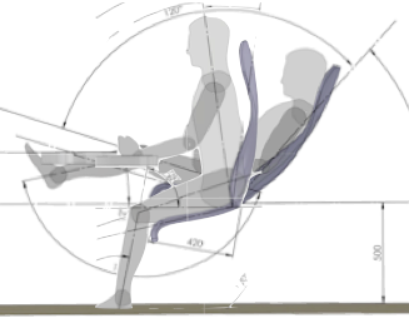 to switch rapidly and easily from a reclined to the upright mode.
to switch rapidly and easily from a reclined to the upright mode.
- This is mainly for convenience but the switch also results in a change of pressure on the disc and this has the added advantage of providing a pumping action which aids disc nutrition.
- No adjustment is allowed to maintain an intermediate position
- These reproduce the conventional adverse sitting posture and should be avoided. (☛Mandal→)
- Their instability can be used for short periods as a form of exercise ( ☛dynamic seating→),
- Particularly for rehabilitation of the Multifidus (☛ muscles→) following an internal derangement at the low lumbar joints. For a fuller account. see ☛Unstable intermediate mode →
Principle 4
Requirement 9. Adjustments should be avoided as far as possible.
This flies in the face of chair designers who are searching for the Holy Grail of infinite adjustability an entirely misplaced endeavour and merely another example of ‘familiarity bias’.ADJUSTMENTS?→
(Requirement 10. Avoid Familiarity bias )