‘Two Tilt, (2T), ‘BiModal’ or (3M) chair
INTRODUCTION
OK. So you are interested in designing a chair which is ergonomically optimised. This involves a certain knowledge of ergonomics and the 2T solution to the problems. An overview is given here but you are advised to trawl through the main corpus of posts and pages.
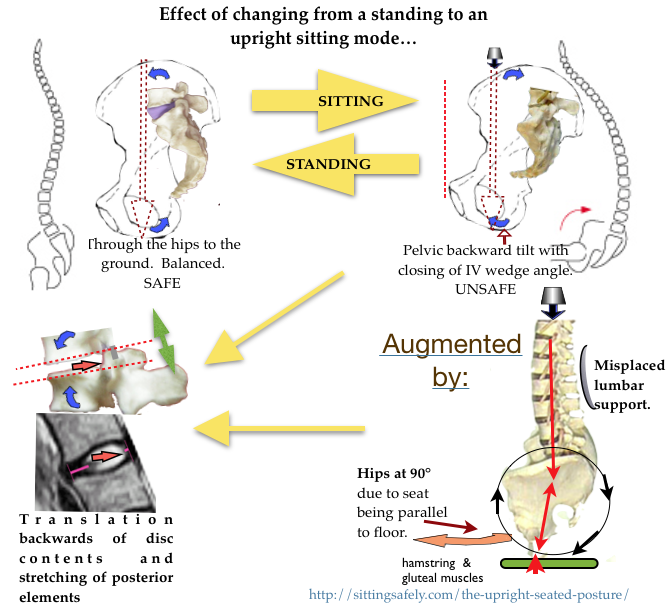
So, what is wrong with an upright chair? See →The upright seated posture.
 Written for designers, first see → Office Chair DESIGN, Ergonomics & Low Lumbar Backache→
Written for designers, first see → Office Chair DESIGN, Ergonomics & Low Lumbar Backache→
 2T so called as there are only 2 stable positions, each at either end of range.
2T so called as there are only 2 stable positions, each at either end of range.
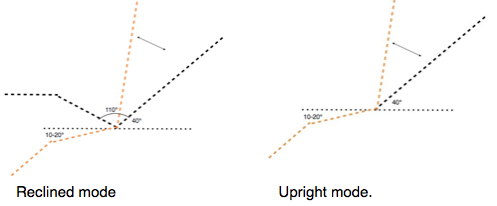
- Reclined mode. A fully supported reclined work position for prolonged work. .
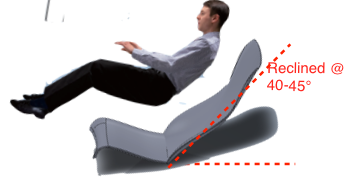 40° from horizontal is assumed to be the most supine reclination as a work mode. Less becomes impractical, (except for the 4M workstation) and more loses some of the axial compression advantage.
40° from horizontal is assumed to be the most supine reclination as a work mode. Less becomes impractical, (except for the 4M workstation) and more loses some of the axial compression advantage.- For more details, see ☛The 2Tilt RECLINED MODE for fully safe sitting.→
- Upright mode for certain short activities and quitting the chair and is the default mode when the chair is unoccupied. ☛2T Upright modes→
- An unstable mid range for quick & easy transition between modes.
 DETAILS & OPTIONS
DETAILS & OPTIONS
The 2T chair consists of (essentially) 2 parts :-
- Carcass shell
- A base, on which the shell is mounted.
- A tilt hinge mechanism.
THE CARCASS/SHELL
- Of fundamental importance to achieve ergonomic optimisation with resulting comfort.
- Reclined mode configuration the’shell’ components are intended to describe a seat’s supporting interface with the human body.
- When completed the Shell Chair forms could be employed to assist in creating an actual shell-based seat in various possible ways:
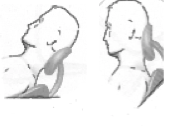
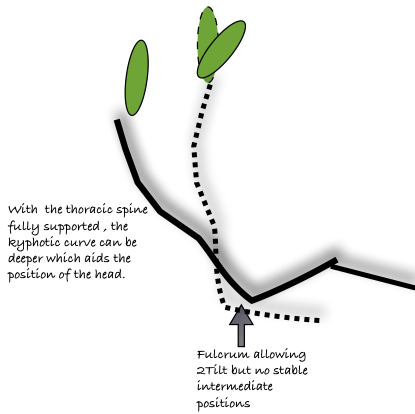
 Shows that a slightly flexed thoracic spine + the upper lumbar joints is not adverse.
Shows that a slightly flexed thoracic spine + the upper lumbar joints is not adverse.- An office version would be narrow with a small telescopic headrest to address height variation and to reduce footprint.
- Iliac (Pelvic) support at correct level and shape to prevent a lumbar ‘sag’.
- Incorrect configuration can engender discomfort (as can be experienced in certain dentists chairs) and more important is potentially dangerous.
- Head support that ensures a forward vision field.
- Variability at head and feet only.
- Leg/foot support.
- a foot rest of some sort is required in the reclined mode .
- Ability to change rapidly to the upright mode.
The alternative upright mode
 This alternative upright mode is for certain short tasks only. Relatively unimportant if the user can be relied on to avoid using this mode for prolonged use.
This alternative upright mode is for certain short tasks only. Relatively unimportant if the user can be relied on to avoid using this mode for prolonged use. - Better use iliac support or a Forward Tilted Seat .
- FTS (forward tilted seat, 20°) ☛ The
 FORWARD TILTED SEAT (FTS).→
FORWARD TILTED SEAT (FTS).→ - Iliac support . ☛ BACK-RESTS. Pelvic support v. Lumbar.→
- ☛ ISCHIAL OFF LOAD system→
- FTS (forward tilted seat, 20°) ☛ The
- With the 2T chair the upright mode is not maintained for long periods and so the feet can be easily tucked under the seat, making height irrelevant…as in the Balans chairs.
- Iliac support is included to prevent lumbar spine sagging in the relaxed mode or if used in the upright mode.
Materials
- Moulded alone in a thin rigid material (as with Aaro Aalto’s ply furniture or the Knoll Saarinen). Graphene is obviously relevant.
- Moulded to form a base shell carrying relatively thin textile/foam skin padding (Eero Saarinen Knoll and Eames Vitra collection).
- As a final form around which a tensile mesh or textile ‘hammock’ design could be generated (Herman Miller Aeron and Knoll Generation chair).
- As a final form around which various upholstered designs could be generated (Knoll Eames or Herman Miller ranges)
- As a final form around which other associated furniture or workstation accessories can be generated (modular office systems)
- Consider Gordon Murray’s system consisting of tubes + composite giving extra strength
http://www.bbc.co.uk/iplayer/episode/b01f11hp/How_to_Go_Faster_and_Influence_People_The_Gordon_Murray_F1_Story/ (Note by Peter Bessey )
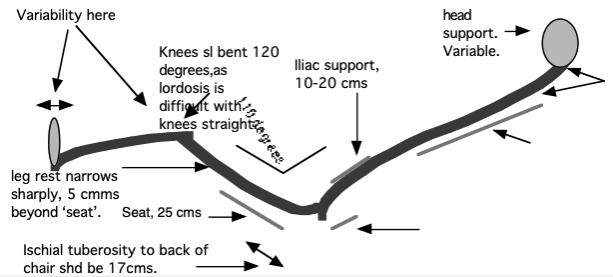
CHAIR SIZE
Largely determined by the the head-rest and foot-rest.
- Shoulder width to allow people with broad shoulders to have full movement without lateral constraint.
- In this assay the headrest is wide to include audio speaker components for home use.
- Also ? size models. See http://www.hermanmiller.com/MarketFacingTech/hmc/solution_essays/assets/se_The_Anthropometrics_of_Fit.pdf . In spite of all their adjustments, bells and whistles, Hermann Miller still has 3 sizes. We should follow with something similar.
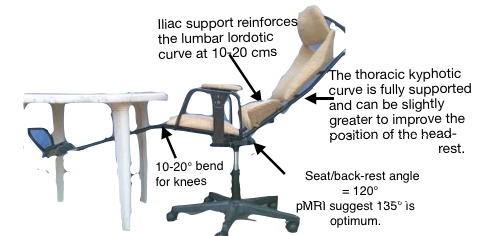
Pelvic (Iliac) support
Pelvic support, developed for upright chairs by John Gorman, an engineer and chiropractor, was in contradistinction to the prevailing ‘lumbar support’. Precise support, shaped to the curve of the iliac crest is applied to the posterior iliac spine and iliac crest of the pelvis. A slight forward
nudge at this point is mechanically efficient in extending the two lowest joints and prevents the pelvis rotating backwards. Pelvic support was designed for upright chairs. As a component of the cacass ‘shell’ it need only be minimal and not adjustable. Intended to 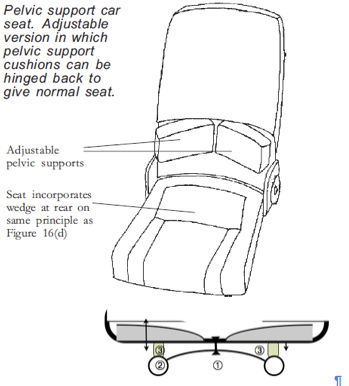 prevent backward pelvic tilting when supine lying. It cease to be ‘pelvic’ and becomes the adverse ‘lumbar’ support above 20 cm from the seat -pan. Do not allow adjustment! See http://sittingsafely.com/pelvic-support/ →
prevent backward pelvic tilting when supine lying. It cease to be ‘pelvic’ and becomes the adverse ‘lumbar’ support above 20 cm from the seat -pan. Do not allow adjustment! See http://sittingsafely.com/pelvic-support/ →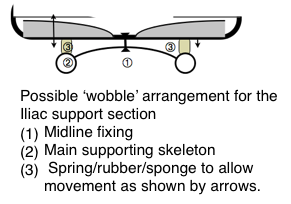
The Forward tilted seat might be preferable.
See ☛ The FORWARD TILTED SEAT (FTS).→
ANGLES & Backrest variability
CAD drawings suggest that the backrest should be hinged to the seat pan to obtain optimal configuration in the 2 modes. Adds to manufacturing cost. These were explored by Peter Bessey as a theoretical exercise in 3D CAD, based on anthropometric (US) data from the well known Henry Dreyfuss book. It commenced around a simple 50percentile male mannequin which was readily available. The information from this investigation, should first be used to generate a totally adjustable Rig device, that should be used for trialling and true research purposes, before any final design concepts are prepared.
With the adoption of the 4M deskless, work-station model the constraints imposed by these angles become largely irrelevant See ☛ OFFICE WORK-STATIONS→
THE SEAT-PAN
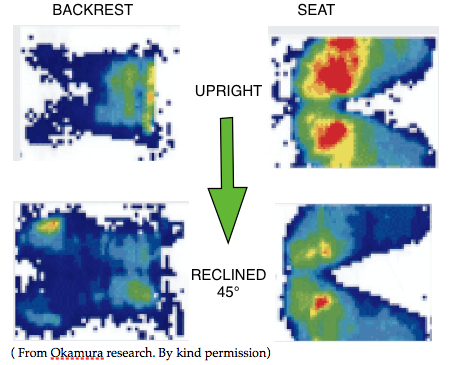 Torso/seat interface pressure studies show that most of the body weight is concentrated at and around the ischial tuberosities. Very little at the thighs, except in the Forward TS mode. Only a ⅓ the thighs require support.
Torso/seat interface pressure studies show that most of the body weight is concentrated at and around the ischial tuberosities. Very little at the thighs, except in the Forward TS mode. Only a ⅓ the thighs require support.
- “stool height.” The term “sitting height” is reserved for the height to the top of the head when seated.
- For men, the median popliteal height is 16.3 inches and for American women it is 15.0 inches.
- The popliteal height, after adjusting for heels, clothing and other issues is used to determine the height of the chair seat. Mass produced chairs are typically 17 inches high.
- For someone seated, the buttock popliteal length is the horizontal distance from the back most part of the buttocks to the back of the lower leg. This anthropometric measurement is used to determine the seat depth.
- Mass produced chairs are typically 15-17 inches deep.
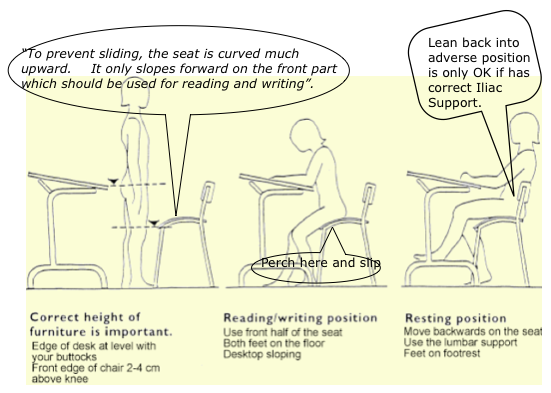 Diagram annotated from Mandal. The Seat height based on Mandal’s ‘Forward tilted seat’ (FTS),by 15-20°.
Diagram annotated from Mandal. The Seat height based on Mandal’s ‘Forward tilted seat’ (FTS),by 15-20°.
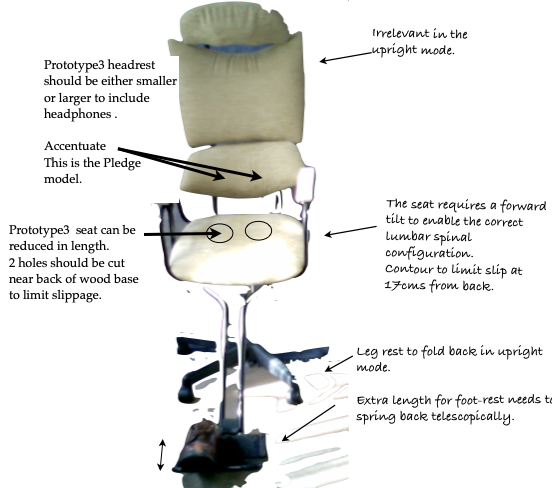 2 holes should be cut near in the wood base to limit slippage with a FTS seat. Position of ‘Butt-pockets’ showed by Okamura research (above).
2 holes should be cut near in the wood base to limit slippage with a FTS seat. Position of ‘Butt-pockets’ showed by Okamura research (above).
Peripheral details
- Essential for full torso support
- Variability is required.
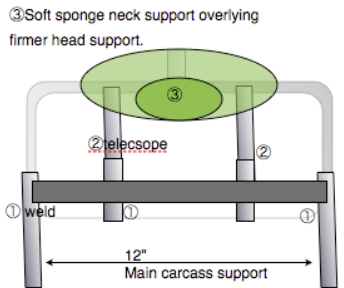
- The headrest needs to be minimalised fo reduce the overall footprint.
- onl.y the base of the skull requires support and the upper neck.
- This only requires a height of 3-4” and a breadth of 9”
- Measurements are shown below.
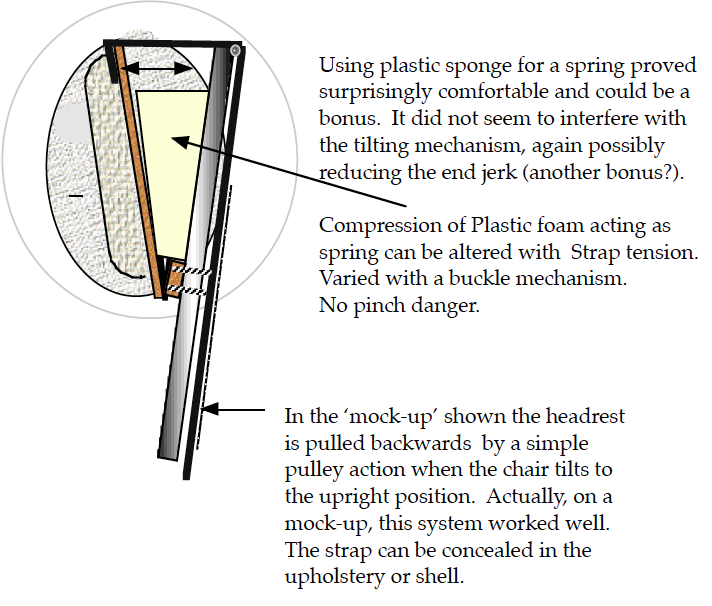
 The head-rest should be adjustable in both
The head-rest should be adjustable in both
- Longitudinal
- A-P directions
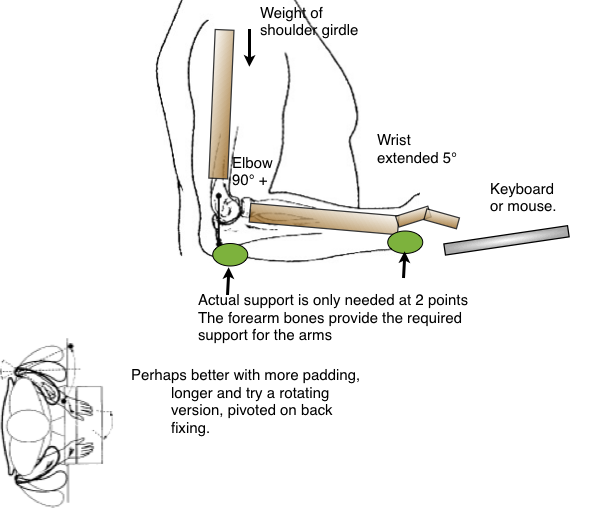
Arm-rests
 Are helpful for typing. They might limit some movement.
Are helpful for typing. They might limit some movement.-
- How should they be mounted?
- On the carcass. This moves with the user and may be an advantage when modes are changed.
-
- On the base. This has the advantage of a fixed point for changing mode. Admittedly this should be unnecessary if the carcass is properly balanced.
FOOT-REST
Optional only if the heels do not rest on the floor or desk bar. This can be arranged if the chair is lowered when in the reclined mode (as in the Okamura chair). I regard this as only acceptable if performed easily without complicated manual adjustments. ( Is it possible to have a mechanism that does this when the user leans backward into the reclined mode?) 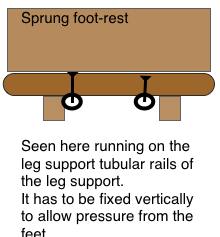 A SPRUNG SOLE MUST BE OPAQUE FOR ISLAMIC SUSCEPTIBILITIES.
A SPRUNG SOLE MUST BE OPAQUE FOR ISLAMIC SUSCEPTIBILITIES.
 A monococque design is probably unsuitable for an office work chair, but may be possible in a deskless design. Ideally the leg/foot-rest should retract or fold back when in the upright mode. A simple system is shown in the garden chair. A similar model can be bought cheaply at B&Q.
A monococque design is probably unsuitable for an office work chair, but may be possible in a deskless design. Ideally the leg/foot-rest should retract or fold back when in the upright mode. A simple system is shown in the garden chair. A similar model can be bought cheaply at B&Q.
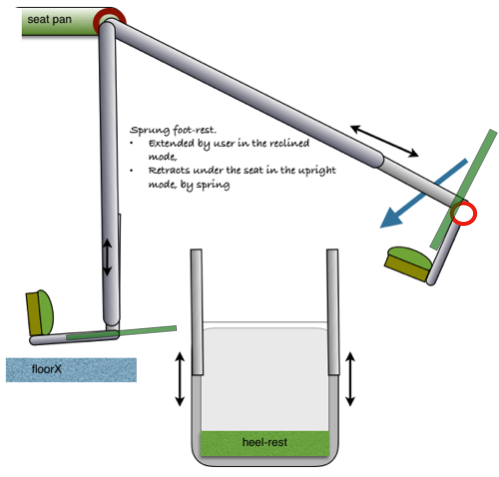 There is no need for the calf support. This could result in DVT. The lower leg bones (tibia& fibula) give the only support required between the thigh at the seat pan and the heel at the foot- rest, However variability of the leg-support is essential.
There is no need for the calf support. This could result in DVT. The lower leg bones (tibia& fibula) give the only support required between the thigh at the seat pan and the heel at the foot- rest, However variability of the leg-support is essential.
TILT-HINGE
- To enable the transition between the stable end-ranges.
- To allow range from 7-135º,
- and that can be used for short periods as a form of comforting exercise, particularly for rehabilitation for an internal derangement at the low lumbar levels. (See ☛ http://sittingsafely.com/exercise/ ).
- The intermediates are unstable.
- Controls are avoided because fixed Mid ranges reproduce the conventional adverse sitting posture.
- Movement is activated by user’s change of posture.
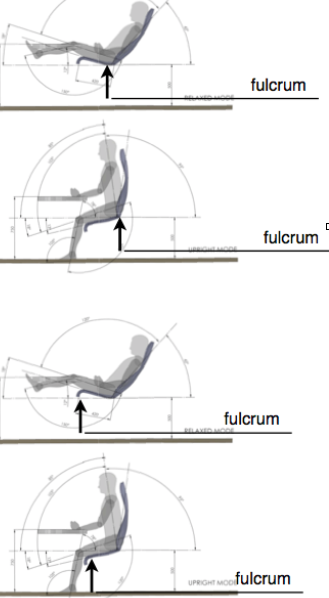 CONCEPTS
CONCEPTS
-
- Concept1. Fulcrum at point of balance under seat, with damping to avoid jolt at extreme of range. Simplest,
- Concept2. Hinge at the anterior border of the seat-pan, using a constant force spring.
- This makes the fwd tilt the default mode. The damped spring allows the chair to fall back and to be lowered to the reclined position.
- Spring tension would have to be adjusted so that user movements would activate the alternative range,
- Also to allow for an user of unusual weight.
-
Thoughts on MONOCOCQUE solutions for home use
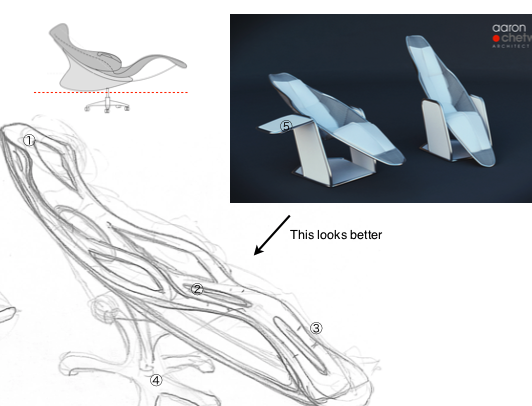
-
- 1/ A cushion for headrest. Fixed variably,
- 2/ Needs to be 2 holes (butt pockets) about 3″ from front edge.
- 3/ See detail notes for foot-rest
- 4/ 5Star base looks wrong for an iconic chair.
- 5/ The drinks flap could rotate to become a computer table.
 Details of the p3 prototype.
Details of the p3 prototype.
To incorporate a heel-rest to the Aaron monocoque design
The tilt-in-space feature allows the whole chair to tilt up to 30 or 60 degrees, while maintaining hip and knee angles. Applies mainly to wheelchairs but note that also pertains in the 2T monocoque concept.
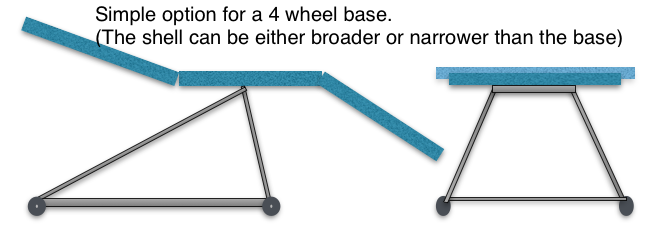
THE 2t BASE
All the 2T prototypes used a standard 5 star base as shown above. A 4 wheel base is easily designed and inexpensively manufactured to various standards. The subject is considered further in the post on the Base→
For user ‘special needs’. A patient would have a shell moulded for the torso that would then be mounted on a suitable version of a 2T chair instead of the standard shell. This addresses the axial compression and pelvic tilt in the reclined mode. In the upright mode the backrest stand away from the torso with a Forward Tilted seat and so becomes irrelevant. But support might be needed and then we would have to think about Gorman’s Iliac version. This is already built into the standard backrest shell, in a reduced form. Plaster-of-Paris’ (POP) casts are commonly made in orthopaedic and physio departments and can be used to form a shell for the individual from fibreglass or other material at no great expense. 3D printing could be relevant. ☛ ‘Special needs’→
- For some ideas & options see :-
- Office Chair DESIGN, Ergonomics & Low Lumbar Backache
- Various chairs. How do they measure up?
- WORK-CHAIRS, a new breed with a reclined mode.
- ROORKEE CHAIRS→
HOSPITAL VERSIONS